Management transboundary underground waters of Kyrgyzstan.
Mandychev A.N.
Just as superficial waters of the rivers cross borders between the states, similarly cross the international borders and underground waters. This process has not received while a due estimation, as is not so obvious, as a outlet of the rivers. Nevertheless, both practical, and the political meaning of a outlet of underground waters is not less important, than superficial outlet.
The problems, characteristic for transboundary outlet of the rivers, practically, do not differ from problems transboundary outlet of underground waters. For underground waters, as well as for superficial, is the pollution and exhaustion of resources characteristic, that requires the appropriate rational management on the basis of monitoring parameters of a condition of underground waters. The exploitation of underground waters in frontier areas requires the interstate coordination, as regards interests of both parties. The quality of underground waters as requires the control, is especial in case of anthropogenous pollution, as, as a rule, underground waters move in hypsometric the lowered parts of hollows and accordingly can transfer pollution through borders.
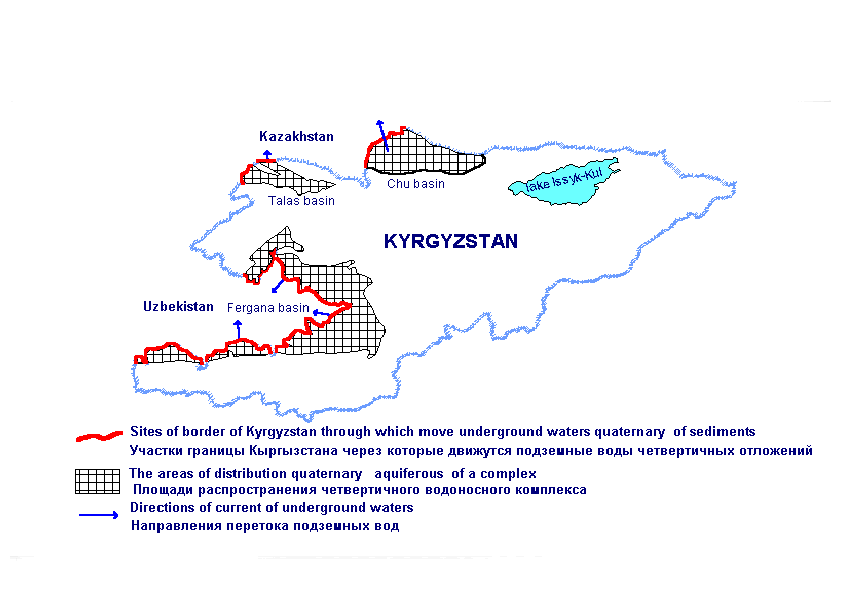
Transboundary underground waters dispose in pools of underground waters, divided by state borders. Underground waters have the continuous mirror, located on certain depth from a surface of ground and move by a continuous flow from areas of a feed to regional bases of unloading, located in the most lowered part of hollows. As a whole, they are similar on transboundary superficial reservoirs, for example lakes, but have the specificity. In particular, as underground waters move in porous space incoherent clastic of rocks, the Speed of movement from shares of meter per day up to the first meters per day, the regional direction of movement of underground waters is constant in time, the structure of a regional flow as, basically, is stable and can will change locally at the expense of anthropogenous influence as evacuate, drainage or additional feed of underground waters by superficial waters. In Kyrgyzstan transboundary underground waters take place on border with Kazakhstan in western part Chu, northwest Talas of pools of underground waters and on border with Uzbekistan in the Fergana pool of underground waters (fig. 1). In all these pools the area of a feed of underground waters is located in territory of Kyrgyzstan, and the regional basis of unloading in territory of the adjoining states, therefore flow of underground waters is directed from territory of Kyrgyzstan on territory of Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan.
Fig.1
The basic resources fresh transboundary underground waters of Kyrgyzstan are located in quaternary sediments by width up to 300 -500 m. In Chu pool of underground waters, through a site of border by extent of 115 km stream on territory of Kazakhstan up to 10 m3/s. of underground waters (most intensive stream during 80 km of northern site of border), in Talas pool on two sites by common extent of 51 km - about 5 m3/s. In the Fergana pool on territory of Uzbekistan through 16 sites of border by common extent of 430 km stream about 25 m3/s. of underground waters.
The basic problems, which can be assumed in connection with transboundary underground waters is stream through border anthropogenous of the polluted underground waters, and as complete or partial interception of renewed natural resources of underground waters by the party located above on a flow of underground waters and reduction of capacitor stocks of underground waters in a frontier zone with reduction of similar stocks on adjoining to the party. For Kyrgyzstan the conflict on the two first problems is possible, the third problem can be initiated by both parties.
Now specified problems have no sharp character, but the preconditions for their genesis exist and can in the long term develop. All this requires organization of the control on quality and quantity of underground waters in frontier areas and duly management of processes conducting to pollution of underground waters and exhaustion of their resources, because of not optimum modes of operation. In this aspect urgent the following basic tasks are:
1) Specification of capacitor stocks of underground waters, rate and structure of movement transboundary flows of underground waters in frontier zones Fergana, Talas, Chu of pools of underground waters.
2) Definition of probable scales of extraction of underground waters in frontier zones, which will not cause drainages aquiferous of horizons and decrease of a level of underground waters of a below allowable limit on adjoining to the party.
3) Monitoring quality and position of a level transboundary flows of underground waters on a case of the claims adjoining of the party on aggravation of quality of underground waters and exhaustion of their resources.
The basic functions of management transboundary underground waters consist in the considered aspect in observation of critical situations in a condition of underground waters (pollution, exhaustion) in frontier areas and acceptance of measures on their prevention and elimination.